Shell Tube Heat Exchanger
Shell Tube Heat Exchanger is a popular class of heat exchanger designs. It consists of a number of tubes mounted inside a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows inside the tubes and the other through the shell.
While flowing they exchange the heats where the cold fluid gains the heat from the hot fluid. So, one cold fluid enters the shell (or tube side or channel side) inlet nozzle and comes out of the outlet nozzle as hot fluid. Consequently, other fluid will become cold in the outlet than in the inlet. The fluid flow inside the Shell Tube Heat Exchanger can be parallel flow or crossflow
The simple design of a shell and tube heat exchanger makes it an ideal cooling solution for a wide variety of applications.

Applications of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
- Cooling of hydraulic fluid
- Oil in engines & transmissions
- Hydraulic power packs
- Power Generation
- HVAC
- Marine Applications
- Pulp and Paper
- Refrigeration
- Pharmaceuticals
- Air Processing and Compressor Cooling
- Metals and Mining
- Removal of process heat and feed water preheating
- Cooling of hydraulic and lube oil
- Cooling of turbine, compressor, and engine
- Condensing process vapor or steam
- Evaporating process liquid or steam
Benefits of Using Heat Exchanger
- Shell and tube heat exchangers have more heat transfer efficiency.
- These heat exchangers are an optimal solution for swimming pool heating, mining machinery, hydraulic power packs, etc.
- These heat exchangers can be easily dismantled, making cleaning and repairs easy.
- They are compact in size.
- The pressure test is simple, allowing easy detection and fixing of tube leaks.
- These heat exchangers are suitable for systems with higher operating temperatures and pressures.
Materials Used for Heat Exchanger
Different materials are used for manufacturing heat exchangers based on the applications. Here are the most frequently materials
Tube’s
- Copper
- Stainless Steel Grade: SS 304, SS 304L, SS 316, SS 316L
- Cupronickel Alloys, 90 – 10 or 70 – 30
- Titanium
- Carbon Steel
- Brass Alloys
- Aluminium Brass
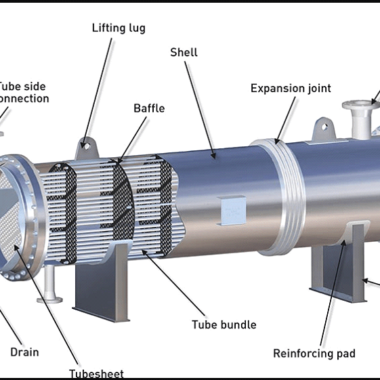
Important Parts of Heat Exchanger
The following are the four most crucial parts of a shell and tube heat exchanger:
- Tube Bundle: A tube bundle consists of tube sheets and tubes. The bundle is held together by baffles and tie rods.
- Shell: The tube bundle is housed within a shell.
- Front Header: Also known as a stationary header, it is the entry point for fluid into the tube side of the exchanger.
- Rear Header: The exit point for fluid from the tube side of the exchanger or the return to the front header.