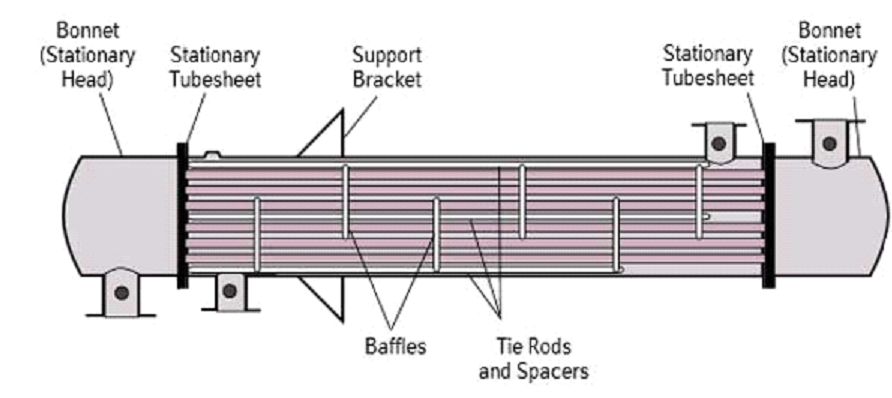
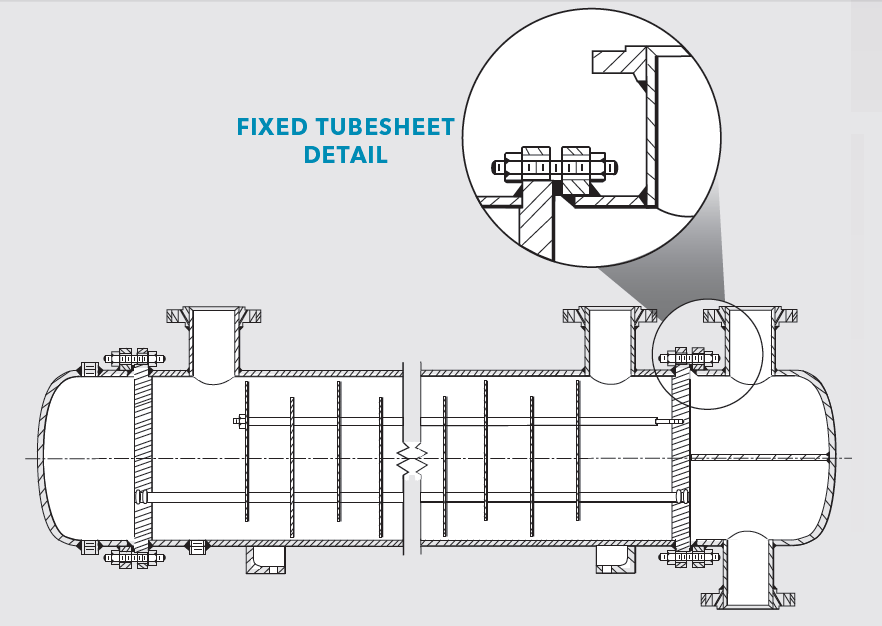
Fixed-Tube Sheet Exchanger
Fixed-Tube Sheet Exchanger It’s a Type of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger. In this type, tubes are fixed in place, meaning they do not move, and the heat transfer occurs between the two fluids through the tube walls. This type of heat exchanger is commonly used in various industrial applications and HVAC systems.
Fixed-tube Sheet Exchanger is typically used for low-pressure applications. This type of exchanger has a number of benefits, including a simple design and easy maintenance. However, it is not as efficient as some other types of exchangers and can be more expensive to operator

How a fixed tube heat exchanger works:
- Tube Configuration:
The tubes are typically arranged in a bundle, and one fluid (often called the process fluid) flows through the tubes, while another fluid (usually called the cooling or heating fluid) flows over the outside of the tubes.
- Fixed Tube Heat Exchanger Heat Transfer:
Heat is transferred from the hot fluid inside the tubes to the colder fluid outside the tubes. This can occur through conduction through the tube walls.
- Fixed Tube Heat Exchanger Applications:
Fixed tube heat exchangers are used in a wide range of industries, such as power plants, chemical processing, petrochemical plants, HVAC systems, and more. They are efficient and can handle high temperatures and pressures.
- Fixed Tube Heat Exchanger Materials:
The materials used for the tubes depend on the specific application and the properties of the fluids involved. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and various alloys.
- Shell-and-Tube Design:
The fixed tube heat exchanger is often referred to as a shell-and-tube heat exchanger. The outer shell contains the tube bundle, and the two fluids flow in a counterflow or parallel flow configuration, depending on the design.
- Fixed Tube Heat Exchanger Maintenance:
One advantage of fixed tube heat exchangers is that they are generally easier to maintain compared to some other types of heat exchangers. However, they may still require periodic inspection and cleaning to ensure optimal performance.
Key components and features of a fixed tube heat exchanger
- Tube Bundle:
The tubes are typically arranged in a bundle and are fixed in place, hence the name “fixed tube.” The fluid inside the tubes is known as the “tube side” fluid.
- Shell
The tubes are housed within a shell, and the fluid flowing over the outside of the tubes is known as the “shell side” fluid.
- Tube Sheets:
The tubes are attached to tube sheets at both ends, forming a sealed connection between the tube side and shell side fluids.
- Baffles:
Baffles are often installed inside the shell to direct the flow of the shell side fluid. They help improve heat transfer efficiency by promoting turbulence and preventing fluid bypass.
- Inlet and Outlet Connections
The heat exchanger has inlet and outlet connections for both the tube side and shell side fluids.
The fixed tube heat exchanger operates on the principle of heat transfer through the tube walls. Heat is transferred from the hot fluid (either inside or outside the tubes) to the cooler fluid through conduction. The effectiveness of the heat exchanger depends on factors such as the flow rates of the fluids, the temperature difference between them, and the thermal conductivity of the tube material.
Each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of fixed tube heat exchanger depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as temperature and pressure conditions, fluid properties, and space constraints. Fixed tube heat exchangers are commonly used in various industrial applications, including HVAC systems, power plants, chemical processing, and refrigeration.