Finned Tube Heat Exchanger
Finned Tube Heat Exchanger generally use air to cool or heat fluids such as air, water, oil or gas, or they can be used to capture or recover waste heat. These heat exchangers can used in a broad range of industries including oil & gas, power generation, marine and HVAC&R.
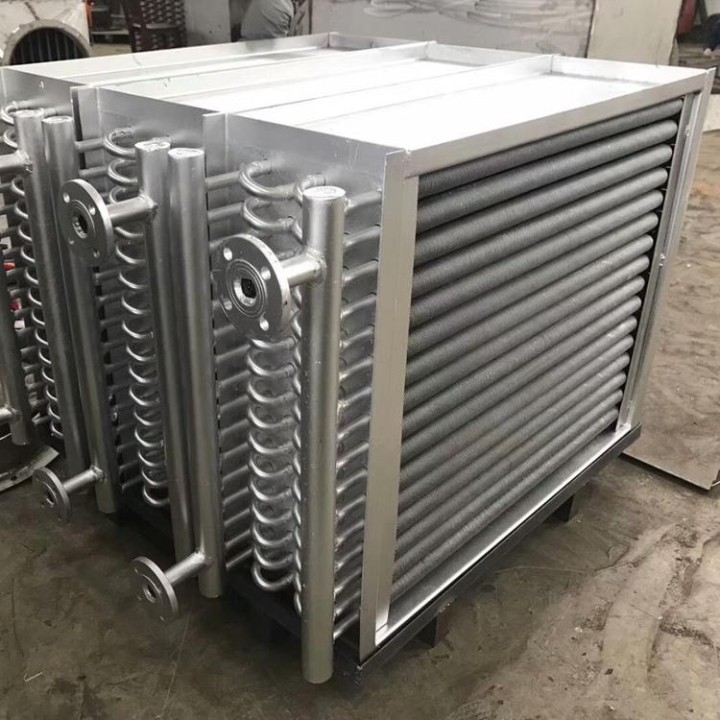

Working Principle of Heat Exchanger
In a finned tube heat exchanger, fins are outside the tubes. The liquid will flow through the finned tube with air or another gas flowing outside, increasing the heat transfer rate due to the greater heat transfer surface area.
The fins on a crossflow tube exchanger are usually circular or square radial fins. Fins should be longitudinal rather than radial in a counterflow or can be parallel flow fin tube exchangers. In an enclosed heat exchanger, finned tubes work as internal tubes.

Finned tube heat exchangers are often used in circumstances where air is the preferred medium for the cooling or heating, particularly where there is limited or poor-quality water.
In a finned tube heat exchanger, heat is exchanged between a thermally efficient fluid that transports heat efficiently, such as a liquid which has some viscosity, and a fluid that does not, such as air or gas with little density. On the ‘air side’, the tube surface is enhanced by the addition of fins or other elements such as looped wires, designed to increase the surface area of the tube and improve its thermal performance.
Fins can range in height (high-fin to low-fin) and the fins can be either pressure connected to the outer surface of the tube or formed into the tube surface.
Depending on the intended duty and the environment in which they are to operate, finned tubes can be manufactured in numerous designs and incorporate a combination of differing materials for both the tubes and the fins. The types and combinations of tubes and fins is significant, but in this article, we will explore only the more common types.
Uses Of Finned Tube Heat Exchanger
- Finned tube heat exchangers are useful when the heat transfer coefficient inside the fluid is higher than the fluid outside the tube.
- Other examples of finned tube air heat exchangers include automobile radiators.
- The truck radiator cools hot water in the tubes by circulating air through them in a crossflow pattern.
- The air conditioner evaporator coil condenses the air traveling through it.
- Finned tube heat exchangers are widely used in industries such as:
- Chemical industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Automobile industry (e.g., heavy truck radiators, car radiators)
- Recent developments in dry cooling for steam power plants have led to the adoption of air-cooled condensers to replace water-cooled ones.
- Different shapes and sizes of fins are designed for specific purposes, such as:
- S-shaped fins used in heavy truck radiators to increase the surface area for heat exchange and enhance heat transfer rates.
- Finned tube heat exchangers with unique fin designs, like S-shaped fins, are considered the best truck radiators in use today.