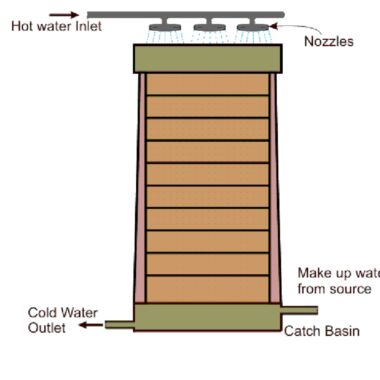
Fanless Cooling Tower
Fanless Cooling Tower does not contain any fan or fill used to cool the water and so it is called fan less and fill less cooling tower. The wooden louvers are used as the side wall of the cooling tower to restrict the water spillage. The outside wind passage enters into the cooling tower and act as the cooling media. The hot water it will be sprayed in the top of the cooling tower with spray nozzles.
This cooling tower is economical as there are fans or fills are used. The best part is that, the maintenance cost of this cooling tower is very less. This is the best payback cooling tower while comparing to other types of the cooling towers. No huge amounts of noise will be produced when the cooling tower is functioning. This cooling tower is designed to meet all your industrial requirements. This cooling tower can be installed where the requirement of the cooling water temperature is not critical. The cooling tower water approach is higher and enough open space is available.

Overview
- Technology: Parallel flow-induced draft technology used in the cooling tower.
- Structural Component: Mild steel hot-dipped galvanized.
- Electricity Savings: Saves electricity and requires no maintenance.
- Construction Material: Fiberglass reinforced plastics.
- Water Distribution: Distributed by fixed roto jet nozzles.
- Capacity: 9 m³/hour, customizable as per customer requirements.
- Fabrication: Factory fabricated and designed for on-site assembly.
- Applications:
- Plastic processing plants
- Light to medium industrial applications
- Chemical plants
- Steel rolling mills
- Process cooling
- Pharmaceutical plants
Natural Draft Cooling Tower
In this type of cooling tower, fan is not used for circulating air but here, by enclosing the heated air in the chimney and it will create pressure difference between heated air and surrounding air. Because of this pressure difference air enters in to the cooling tower. It requires large hyperbolic tower, so capital cost is high but operating cost is low because of absence of electrical fan. There are two types of natural draught cooling tower, rectangular timber tower and reinforced concrete hyperbolic tower.
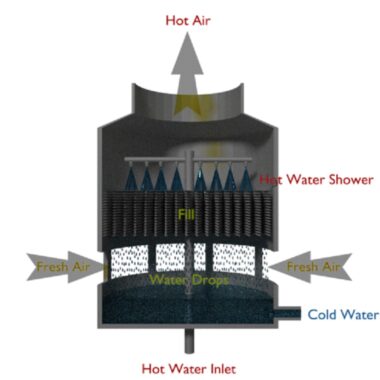
A cooling tower is an open direct contact type heat exchanger where hot water from system or condenser gets cooled by direct contact with fresh air. Cooling towers use the principle of evaporation of water against the air flow. Hot water is sprayed from the nozzles for increasing the heat transfer surface area. The temperature and humidity of the air get increased after direct contact heat transfer between hot water and fresh air. The warm and moist air being less dense goes to the top of the tower, and cold water gets collected at the bottom of the tower. Fresh air is supplied from the bottom of the cooling tower due to the density difference between hot air inside the stack and atmospheric air outside the cooling tower.
Generally, we use cooling towers in power stations, oil refineries, petrochemical plants, and natural gas plants to remove heat from circulating water system. The below-shown diagram represents the process of cooling towers.
Natural Draft Cooling Tower
In natural draft cooling towers, air flow is obtained by pressure difference obtained from its structure i.e. chimney effect. Warm and moist air (less dense) after heat transfer will go out of the cooling tower to the atmosphere, creating to flow in fresh air (denser). The flow of air occurs due to the density difference between the warm (less dense) air inside the cooling tower and relatively cool (denser) ambient air outside the cooling tower.
Pressure head developed due to the density difference between the cold air and warm air is given by formula,
Where H is the height of the tower above the fill,
ρo is the density of outside air,
ρi is the density of inside air,
g is the gravity constant.
In order to provide sufficient airflow, the height of the cooling tower H must be large as the density difference (ρo – ρi) is not quite large. These towers tend to be very large both in height (around 200 meters) and in cross-section so that the amount of water to flow in each tower is also large. Cooling towers are in generally cylindrical (made of wood) or hyperbolic (made of concrete) shape. The hyperbolic shape of the cooling tower made of a concrete shell which is critical in heat transfer process occurring within the cooling tower. These hyperbolic shape cooling towers offer superior structural strength and resistance to high ambient wind loadings than the cylindrical shape.
Natural draft cooling towers are generally preferred in
⦁ Cool and humid climates (low wet-bulb temperature and high relative humidity)
⦁ Heavy winter loads
Working Principle of Natural Draft Cooling Towers
The hot water that is to be cooled in the cooling tower is pumped to the top of the cooling tower at the hot water inlet. The hot water inlet is connected to a series of nozzles which spray this water over the fill material (provides a large contact surface area for heat transfer). Fresh air is induced by the open structure at bottom of the tower and then the air flows in the upward direction for direct contact heat transfer between warm water and air. The hot water liberates heat after direct contact with fresh air and some of the water gets evaporated and cold water gets collected at the bottom of the tower. Warm and moist air will be discharged from the top of the tower into the atmosphere.
Advantages of Natural Draft Cooling Towers
- No electrical fan is installed so power saving
- No corrosion problems
- Maintenance is low
- No recirculation of air occurs due to high stack outlet
Disadvantages of Natural Draft Cooling Towers
- Huge water flow required.
- These require a large area.
- Its performance depends on wind velocity and direction.